
For about a decade now, mathematicians and mathematics educators have been weighing in on a particular debate rooted in school mathematics that shows no signs of abating.
The debate, covered by Slate, Popular Mechanics, The New York Times and many other outlets, is focused on an equation that went so “viral” that it, eventually, was lumped with other phenomena that have “broken” or “divided” the internet.
On the off chance you’ve yet to weigh in, now would be a good time to see where you stand. Please answer the following:
8÷2(2+2)=?
If you’re like most, your answer was 16 and are flabbergasted someone else can find a different answer. Unless, that is, you’re like most others and your answer was 1 and you’re equally confused about seeing it another way. Fear not, in what follows, we will explain the definitive answer to this question — and why the manner in which the equation is written should be banned.
Our interest was piqued because we have conducted research on conventions about following the order of operations — a sequence of steps taken when faced with a math equation — and were a bit befuddled with what all the fuss was about.
Clearly, the answer is…
Two viable answers to one math problem? Well, if there’s one thing we all remember from math class: that can’t be right!
Many themes emerged from the plethora of articles explaining how and why this “equation” broke the internet. Entering the expression on calculators, some of which are programmed to respect a particular order of operations, was much discussed.
Others, hedging a bit, suggest both answers are correct (which is ridiculous).
The most dominant theme simply focused on implementation of the order of operations according to different acronyms. Some commentators said people’s misunderstandings were attributed to incorrect interpretation of the memorized acronym taught in different countries to remember the order of operations like PEMDAS, sometimes used in the United States: PEMDAS refers to applying parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition and subtraction.
A person following this order would have 8÷2(2+2) become 8÷2(4) thanks to starting with parentheses. Then, 8÷2(4) becomes 8÷8 because there are no exponents, and “M” stands for multiplication, so they multiply 2 by 4. Lastly, according to the “D” for division, they get 8÷8=1.
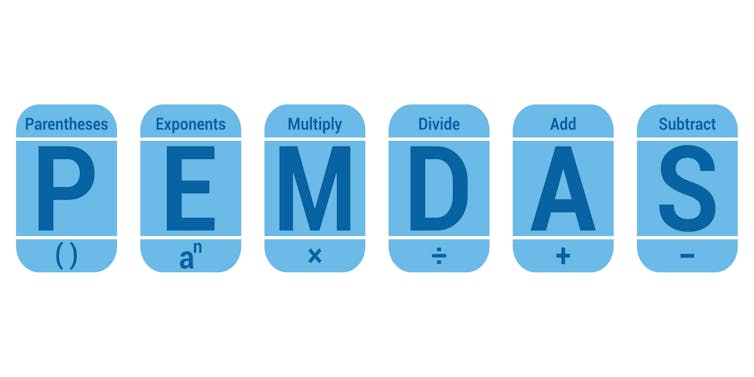
By contrast, Canadians may be taught to remember BEDMAS, which stands for applying brackets, exponents, division, multiplication, addition and subtraction. Someone following this order would have 8÷2(2+2) become 8÷2(4) thanks to starting with brackets (the same as parentheses). Then, 8÷2(4) becomes 4(4) because (there are no exponents) and “D” stands for division. Lastly, according to the “M” for multiplication, 4(4)=16.
Do not omit multiplication symbol
For us, the expression 8÷2(2+2) is syntactically wrong.
Key to the debate, we contend, is that the multiplication symbol before the parentheses is omitted.
Such an omission is a convention in algebra. For example, in algebra we write 2x or 3a which means 2 × x or 3 × a. When letters are used for variables or constants, the multiplication sign is omitted. Consider the famous equation e=mc2, which suggests the computation of energy as e=m×c2.
The real reason, then, that 8÷2(2+2) broke the internet stems from the practice of omitting the multiplication symbol, which was inappropriately brought to arithmetic from algebra.
Inappropriate priority
In other words, had the expression been correctly “spelled out” that is, presented as “8 ÷ 2 × (2 + 2) = ? ”, there would be no going viral, no duality, no broken internet, no heated debates. No fun!
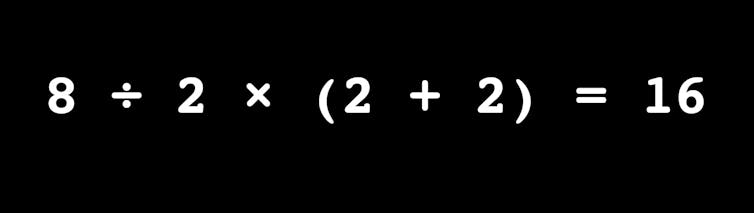
Ultimately, omission of the multiplication symbol invites inappropriate priority to multiplication. All commentators agreed that adding the terms in the brackets or parentheses was the appropriate first step. But confusion arose given the proximity of 2 to (4) relative to 8 in 8÷2(4).
We want it known that writing 2(4) to refer to multiplication is inappropriate, but we get that it’s done all the time and everywhere.
Nice symbol for multiplication
There is a very nice symbol for multiplication, so let’s use it: 2 × 4. Should you not be a fan, there are other symbols, such as 2•4. Use either, at your pleasure, but do not omit.
As such, for the record, the debate over one versus 16 is now over! The answer is 16. Case closed. Also, there should have never really been a debate in the first place.
Egan J Chernoff, Professor of Mathematics Education, University of Saskatchewan and Rina Zazkis, Professor, Faculty of Education, Simon Fraser University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.